Overpressure flowchart
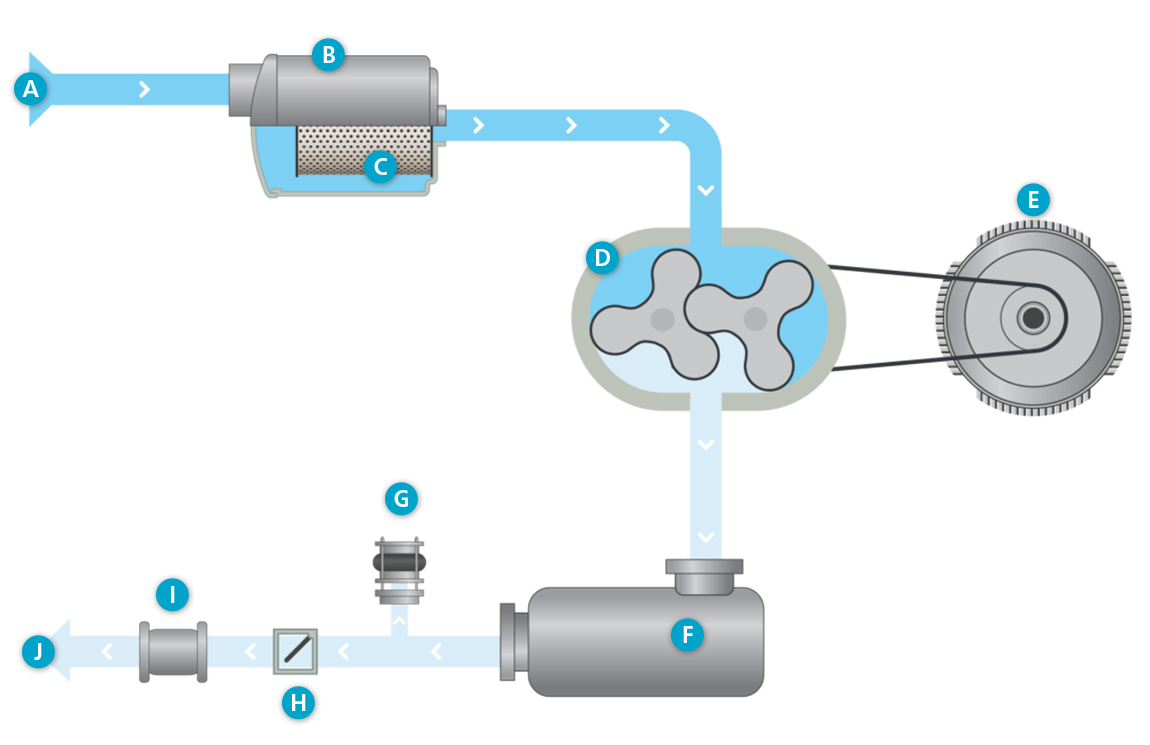
A. Air inlet
B. Intake silencer
C. Intake filter
D. Oil-free lobe blower element
E. Motor
F. Pulsation damper
G. Vacuum safety valve
H. Check valve
I. Compensator
J. Air out
 Atmospheric air
Atmospheric air
 Compressed air
Compressed air
Cooling flow
- A fan forces fresh process and ventilation air in the canopy, through a noise attenuating baffle system.
- Cubicle ventilation air is mixed with the canopy ventilation air.
- The motor cooling fan circulates this fresh canopy air over the motor housing, The motor fan-cowl ensures that air flowing over the motor cooling fins.
- The forced ventilation flow through the canopy removes the heat radiated by the blower core.
- The hot canopy air can leave the canopy through a grating at the side panel.
- The hot air blown out by the startup and safety valve is ducted straight out of the canopy to avoid canopy heating.
Process flow (intake)
- A fan forces fresh process and ventilation air in the canopy, through a noise attenuating baffle system.
- Air is filtered prior to entering the lobe blower element. The filter housing reduces the inlet pulsations.
- The lobe blower element moves air from inlet to outlet.
- Discharge silencer reduces the pressure pulsation levels to the minimum.
- At start-up, the blow-off valve is “open” for smooth unit start-up. That valve closes itself, pushed by the increased air pressure.
Process flow (discharge)
- As soon as the blow-off valve is closed, air pressure increases further, resulting in enough force to push the check-valve open.
- Air is delivered to the system.